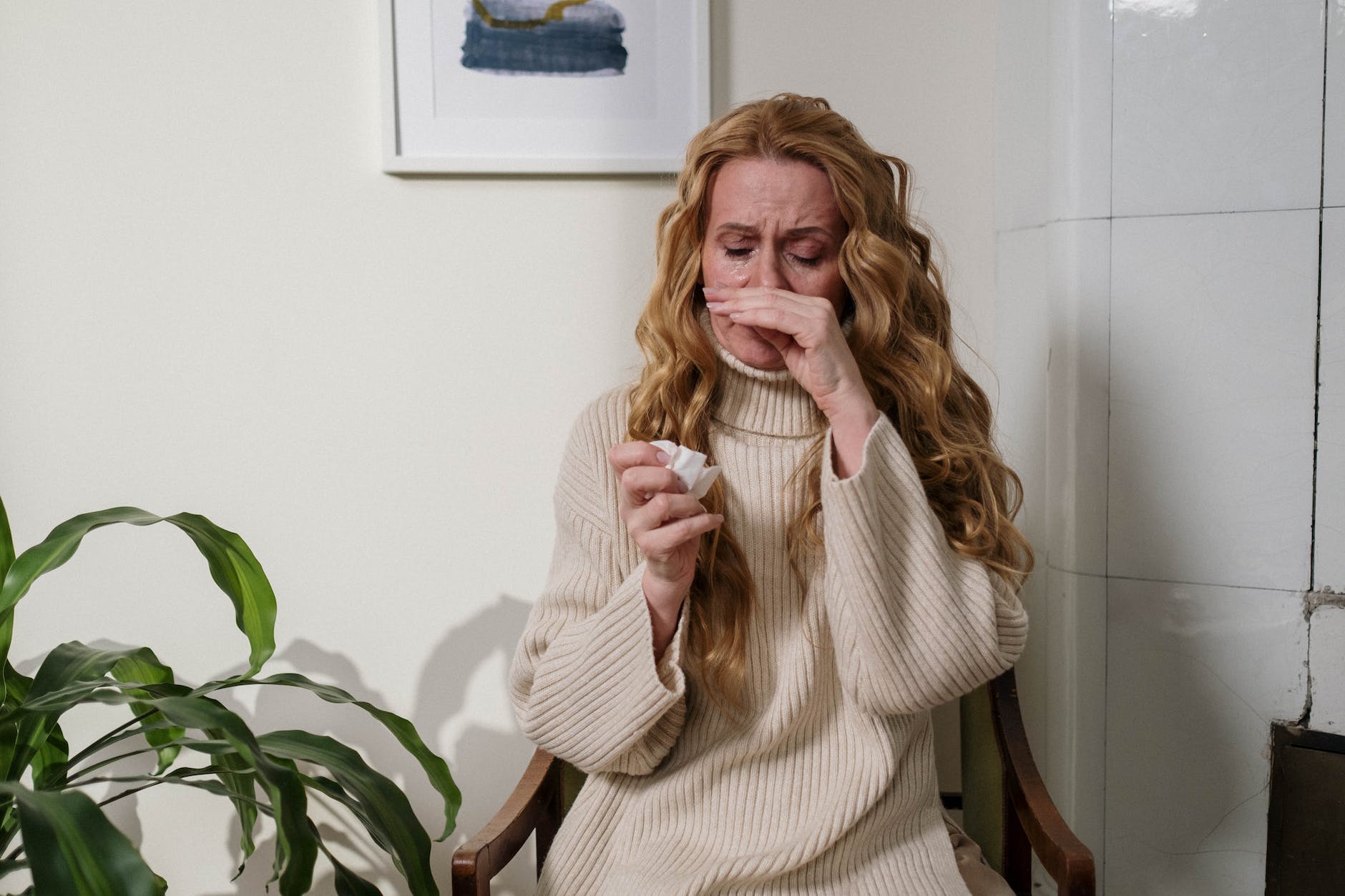
Seasonal allergies, often referred to as hay fever or allergic rhinitis, can make certain times of the year particularly challenging for many individuals. With symptoms ranging from sneezing, nasal congestion, and runny nose to itchy eyes and throat irritation, these allergies can impact your daily activities and overall quality of life. However, healthcare professionals frequently recommend antihistamines as a go-to remedy. Let’s explore why.
Understanding Allergies and Histamine
Before diving into why antihistamines are effective, it’s crucial to understand the underlying cause of allergy symptoms. When you have seasonal allergies, your immune system identifies a harmless airborne substance, such as pollen, as a threat. In response, your body produces chemicals called histamines as part of an inflammatory response to fend off the perceived intruder.
Histamines attach to receptors in blood vessels, causing them to enlarge. This reaction leads to common allergy symptoms as the body attempts to expel the allergen. Histamine’s effects on nasal tissues result in swelling and congestion, while its action in the eyes causes itching and watering. This is where antihistamines come into play.
The Role of Antihistamines
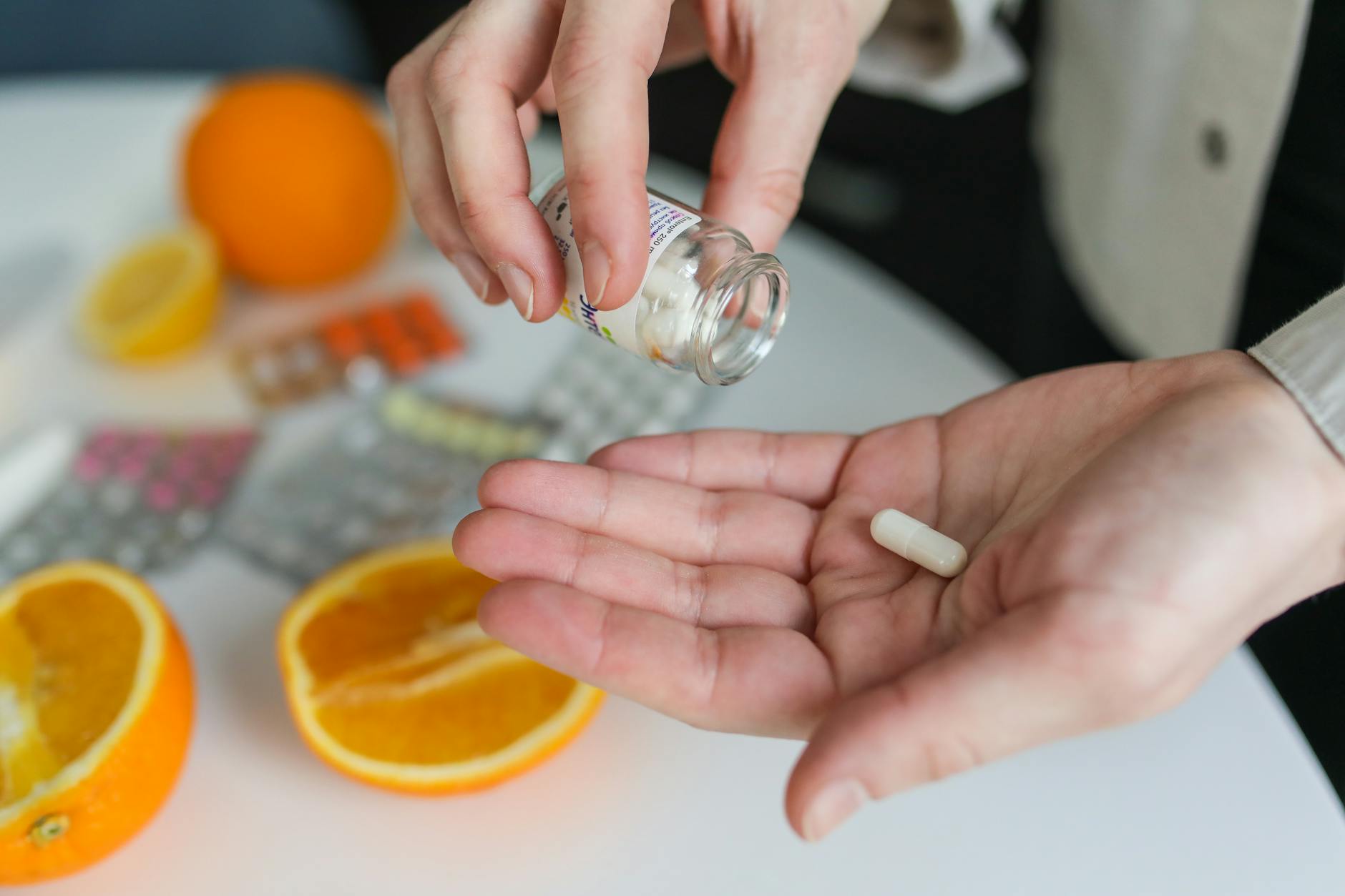
Antihistamines are drugs specifically designed to block histamine from binding to its receptors. By hindering this interaction, antihistamines reduce or even eliminate the symptoms caused by the body’s overreaction to allergens.
Different Types of Antihistamines
There are several types of antihistamines available:
- First-generation antihistamines: These can be very effective but often cause drowsiness. They include options like diphenhydramine (Benadryl) and chlorpheniramine (Chlor-Trimeton).
- Second-generation antihistamines: Developed to cause less sedation, these are more suitable for daytime use and include loratadine (Claritin), fexofenadine (Allegra), and cetirizine (Zyrtec).
The Benefits of Taking Antihistamines for Allergies
- Symptom Relief: Antihistamines can quickly alleviate itching, sneezing, and runny nose, improving your ability to perform daily activities without discomfort.
- Reduced Inflammation: By blocking histamine, antihistamines help to reduce inflammation and swelling of nasal passages, providing a clearer airway to breathe.
- Versatility: Available in various forms such as tablets, liquids, nasal sprays, and eye drops, antihistamines offer a mode of application that can target specific symptoms.
When to Take Antihistamines
For best results, doctors often advise taking antihistamines before you’re exposed to allergens. This preventive approach can help keep histamine release at bay, lessening symptom severity. However, antihistamines can also be used after symptoms have developed to offer relief.
Safe Usage and Consultation
While antihistamines are generally safe, they can interact with other medications and aren’t suitable for everyone. First-generation antihistamines might impair your ability to drive or operate heavy machinery due to their sedative effects. Second-generation antihistamines are less likely to cause drowsiness, making them a favored choice for many.
Before starting any new medication, it’s imperative to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure it’s appropriate for your specific health profile and to discuss any potential side effects or interactions.
Conclusion
Seasonal allergies can be a significant nuisance, but the judicious use of antihistamines can offer much-needed relief. By understanding how these drugs work and under the guidance of a physician, you can manage your allergies effectively and reclaim the joys of every season. With a range of options available, finding the right antihistamine can make all the difference in your fight against hay fever.