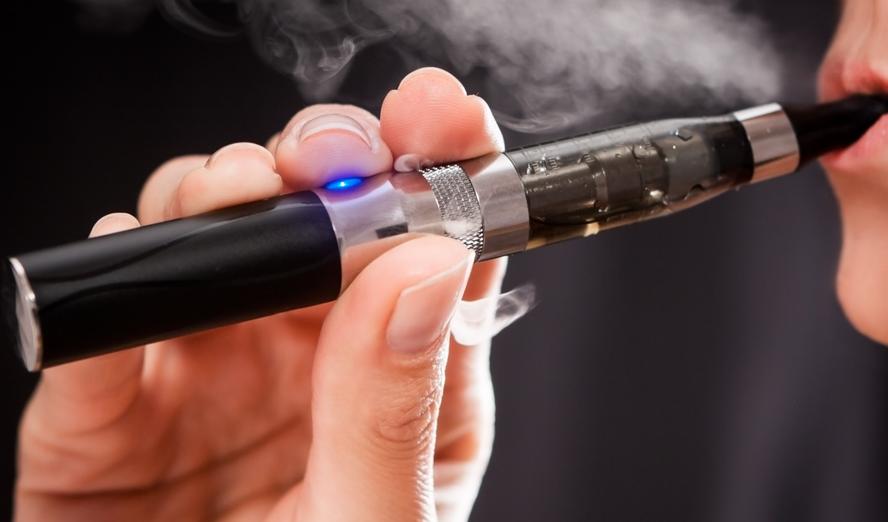
Electronic cigarettes, or e-cigarettes, are often advertised as a safer alternative to traditional tobacco smoking. However, recent research suggests that switching to e-cigarettes might not be the heart-healthy choice that many assume. A significant body of evidence indicates that e-cigarette use can increase the risk of heart failure by 19%.
Understanding E-Cigarettes
E-cigarettes are battery-operated devices that heat a liquid, usually containing nicotine, flavorings, and other chemicals, to create a vapor that the user inhales. While they avoid some of the tar and other harmful substances found in traditional cigarette smoke, e-cigarettes can still introduce a range of potentially dangerous chemicals into the body.
The Study on Heart Failure Risk
A landmark study conducted on the health impacts of e-cigarettes found that individuals who use e-cigarettes are at a higher risk of heart failure than non-users. This comprehensive research evaluated the health outcomes of thousands of individuals over several years, accounting for various lifestyle factors and medical histories.
Key Findings:
- E-cigarette users have a 19% increased risk of heart failure compared to non-users.
- This risk persists even when controlling for traditional cigarette use and other heart-related risk factors.
How E-Cigarettes Affect the Heart
The increased heart failure risk associated with e-cigarette use can be attributed to several factors:
- Nicotine: This addictive substance can increase blood pressure and heart rate, leading to stress on the heart muscle.
- Flavoring Chemicals: Certain flavoring compounds have been linked to cardiotoxicity, which may damage heart cells.
- Heavy Metals and Particulates: The vapors can contain tiny particles and heavy metals that, when inhaled, may contribute to heart disease.
Implications for Public Health
This new evidence challenges the perception that e-cigarettes are a risk-free nicotine alternative. Health professionals and public health campaigns need to incorporate these findings to ensure that the public is correctly informed about the potential risks associated with e-cigarette use.
Conclusion
While further research is necessary to fully understand the long-term effects of e-cigarettes, current data indicate that these devices are not without risk. Specifically, the increased risk of heart failure cannot be overlooked. Individuals considering e-cigarettes as a smoking alternative should be aware of these risks and discuss them with a healthcare professional.
As our understanding of e-cigarettes continues to evolve, it is crucial that users stay informed and weigh the risks against any perceived benefits. Making informed choices is essential for heart health and overall well-being.